Experimental data assessment and model parameters optimisation¶
Data preparation¶
The first step to generate three-dimensional (3D) models of a specific genomic regions is to filter columns with low counts and with no diagonal count in order to remove outliers or problematic columns from the interaction matrix. The particles associated with the filtered columns will be modelled, but will have no experimental data applied.
Here we load the data previous data already normalised.
from pytadbit import load_chromosome
from pytadbit.parsers.hic_parser import load_hic_data_from_bam
crm = load_chromosome('results/fragment/chr3.tdb')
B, PSC = crm.experiments
B, PSC
(Experiment mouse_B (resolution: 100 kb, TADs: 96, Hi-C rows: 1601, normalized: None), Experiment mouse_PSC (resolution: 100 kb, TADs: 118, Hi-C rows: 1601, normalized: None))
Load raw data matrices, and normalized matrices
base_path = 'results/fragment/{0}_both/03_filtering/valid_reads12_{0}.bam'
bias_path = 'results/fragment/{0}_both/04_normalizing/biases_{0}_both_{1}kb.biases'
reso = 100000
chrname = 'chr3'
cel1 = 'mouse_B'
cel2 = 'mouse_PSC'
hic_data1 = load_hic_data_from_bam(base_path.format(cel1),
resolution=reso,
region='chr3',
biases=bias_path.format(cel1, reso // 1000),
ncpus=8)
hic_data2 = load_hic_data_from_bam(base_path.format(cel2),
resolution=reso,
region='chr3',
biases=bias_path.format(cel2, reso // 1000),
ncpus=8)
(Matrix size 1601x1601) [2020-02-06 16:39:39] - Parsing BAM (101 chunks) [2020-02-06 16:39:39] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... 50/101 .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... 100/101 . 101/101 - Getting matrices [2020-02-06 16:39:42] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... 50/101 .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... 100/101 . 101/101 (Matrix size 1601x1601) [2020-02-06 16:39:46] - Parsing BAM (101 chunks) [2020-02-06 16:39:46] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... 50/101 .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... 100/101 . 101/101 - Getting matrices [2020-02-06 16:39:50] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... 50/101 .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... 100/101 . 101/101
B.load_hic_data([hic_data1.get_matrix(focus='chr3')])
B.load_norm_data([hic_data1.get_matrix(focus='chr3', normalized=True)])
PSC.load_hic_data([hic_data2.get_matrix(focus='chr3')])
PSC.load_norm_data([hic_data2.get_matrix(focus='chr3', normalized=True)])
It is a good practice to check that the data is there:
crm.visualize(['mouse_B', 'mouse_PSC'], normalized=True, paint_tads=True)
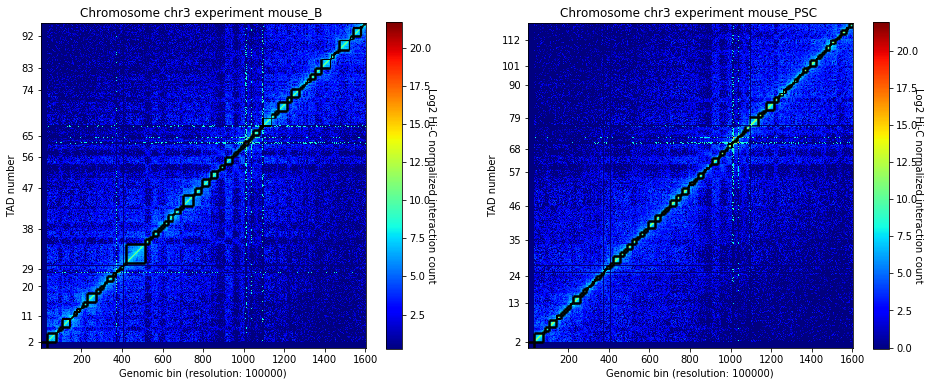
Focus on the genomic region to model.
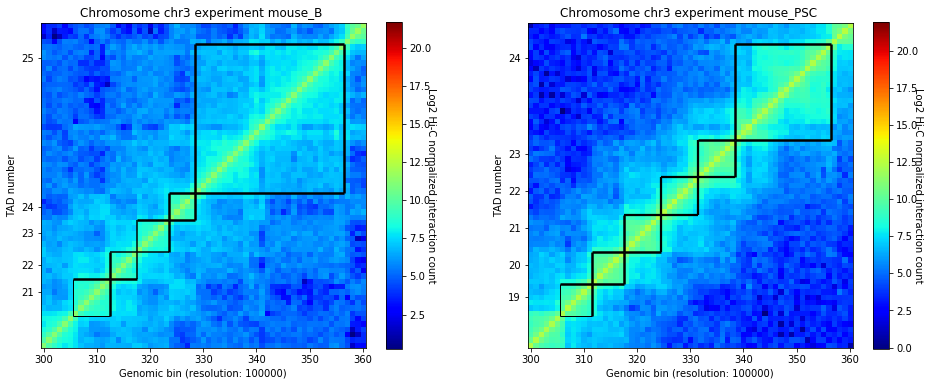
crm.visualize(['mouse_B', 'mouse_PSC'], normalized=True, paint_tads=True, focus=(300, 360))
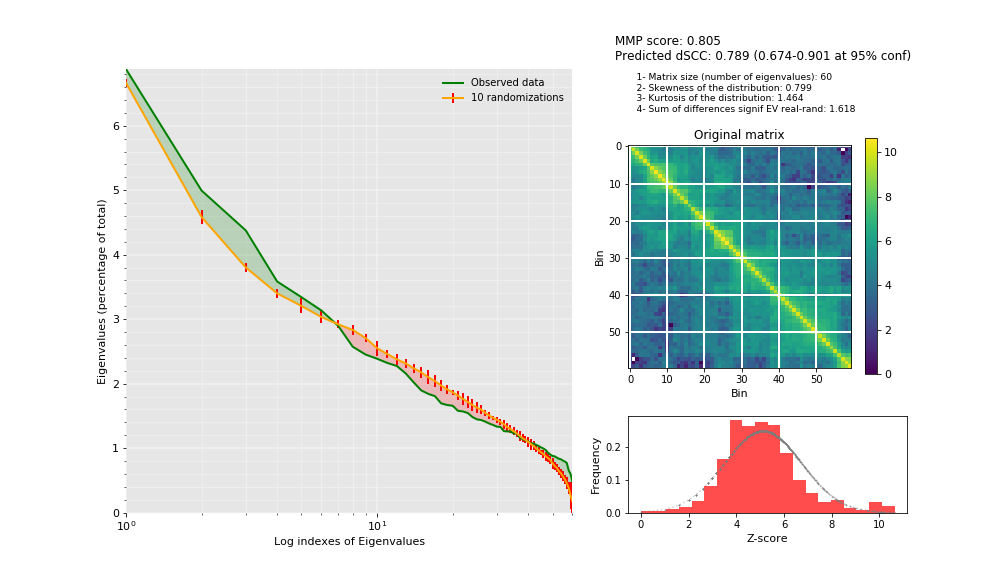
Data modellability assessment via MMP score¶
We can use the Matrix Modeling Potential (MMP) score (Trussart M. et al. Nature Communication, 2017) to identify a priori whether the interaction matrices have the potential of being use for modeling. The MMP score ranges from 0 to 1 and combines three different measures: the contribution of the significant eigenvectors, the skewness and the kurtosis of the distribution of Z-scores.
from pytadbit.utils.three_dim_stats import mmp_score
mmp_score(hic_data1.get_matrix(focus='chr3:30000000-36000000'),
savefig='results/fragment/{0}_both/mmp_score.png'.format(cel1))
(0.8049308283731964, 0.7885888244416531, 0.6736346044021908, 0.9006021702003049)
Data Transformation and scoring function¶
This step is automatically done in TADbit. A a weight is generated for each pair of interactions proportional to their interaction count as in formula:
The raw data are then multiplied by this weight. In the case that multiple experiments are used, the weighted interaction values are normalised using a factor (default set as 1) in order to compare between experiments. Then, a Z-score of the off-diagonal normalised/weighted interaction is calculated as in formula:
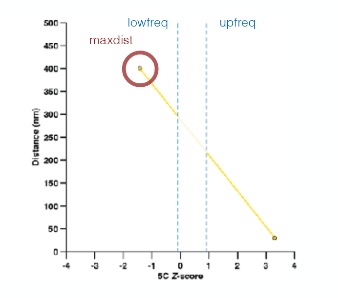
The Z-scores are then transformed to distance restraints. To define the type of restraints between each pair of particles. we need to identified empirically three optimal parameters (i) a maximal distance between two non-interacting particles (maxdist), (ii) a lower-bound cutoff to define particles that do not interact frequently (lowfreq) and (iii) an upper-bound cutoff to define particles that do interact frequently (upfreq). In TADbit this is done via a grid search approach.
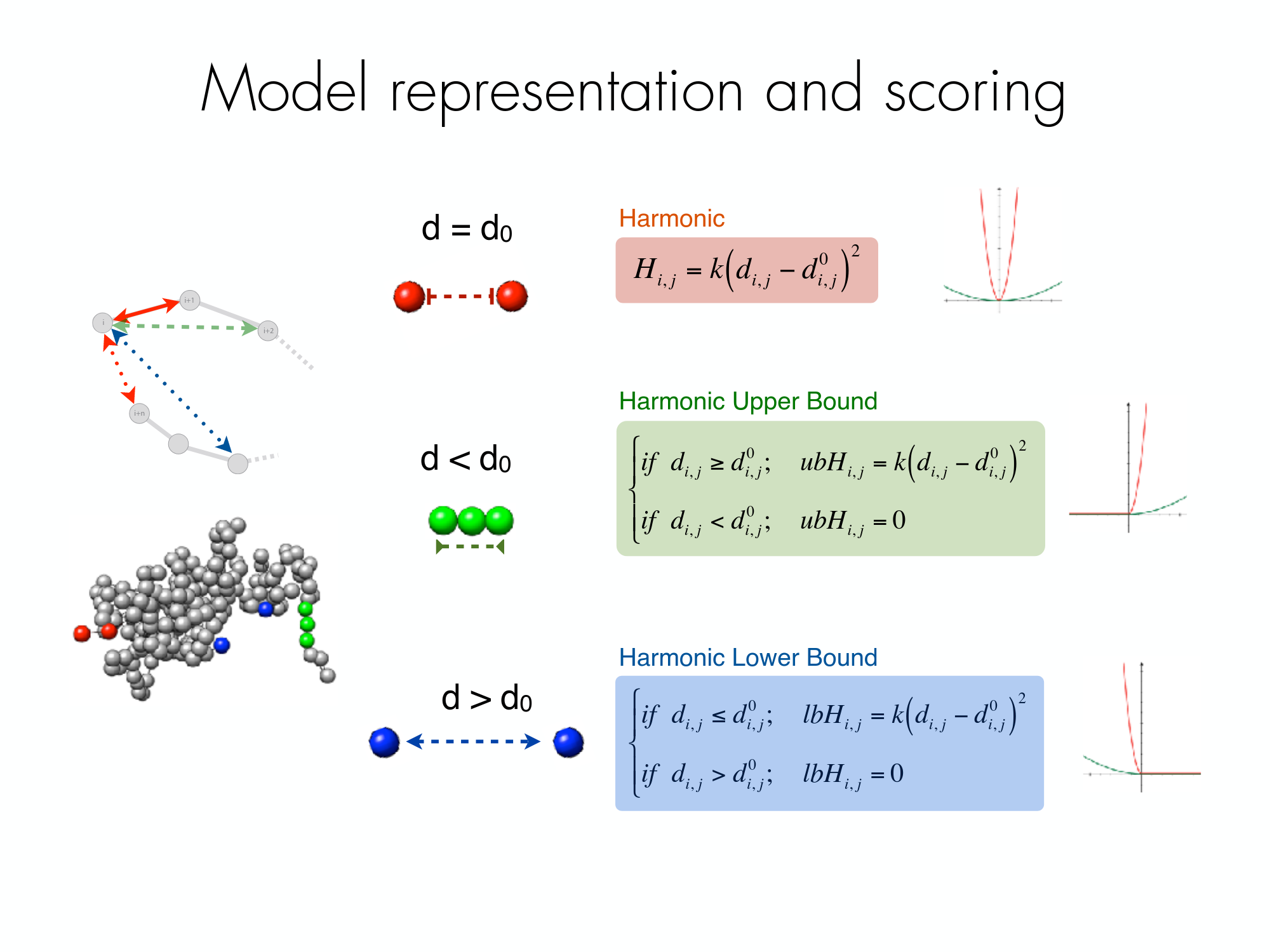
The following picture shows the different component of the scoring funtion that is optimised during the Monte Carlo simulated annealing sampling protocol. Two consecutive particles are spatially restrained by a harmonic oscillator with an equilibrium distance that corresponds to the sum of their radii. Non-consecutive particles with contact frequencies above the upper-bound cutoff are restrained by a harmonic oscillator at an equilibrium distance, while those below the lower-bound cutoff are maintained further than an equilibrium distance by a lower bound harmonic oscillator.
Optimization of parameters¶
We need to identified empirically (via a grid-search optimisation) the optimal parameters for the mdoelling procedure:
maxdist: maximal distance assosiated two interacting particles.
upfreq: to define particles that do interact frequently (defines attraction)
lowfreq: to define particles that do not interact frequently ( defines repulsion)
dcutoff: the definition of “contact” in units of bead diameter. Value of 2 means that a contact will occur when 2 beads are closer than 2 times their diameter. This will be used to compare 3D models with Hi-C interaction maps.
Pairs of beads interacting less than lowfreq (left dashed line) are penalized if they are closer than their assigned minimum distance (Harmonic lower bound). Pairs of beads interacting more than ufreq (right dashed line) are penalized if they are further apart than their assigned maximum distance (Harmonic upper bound). Pairs of beads which interaction fall in between lowfreq and upfreq are not penalized except if they are neighbours (Harmonic)
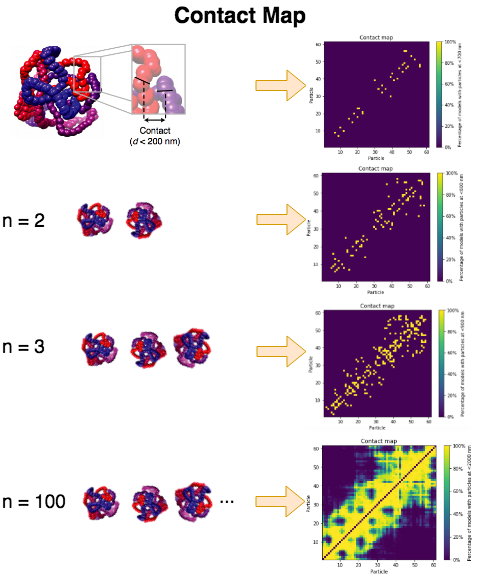
In the parameter optimization step we are going to give a set of ranges for the different search parameters. For each possible combination TADbit will produce a set of models.
In each individual model we consider that two beads are in contact if their distance in 3D space is lower than the specified distance cutoff. TADbit builds a cumulative contact map for each set of models as shown in the schema below. The contact map is then compared with the Hi-C interaction experiment by means of a Spearman correlation coefficient. The sets having higher correlation coefficients are those that best represents the original data.
opt_B = B.optimal_imp_parameters(start=300, end=360, n_models=40, n_keep=20, n_cpus=8,
upfreq_range=(0, 0.6, 0.3),
lowfreq_range=(-0.9, 0, 0.3),
maxdist_range=(1000, 2000, 500),
dcutoff_range=[2, 3, 4])
Optimizing 61 particles num scale kbending maxdist lowfreq upfreq dcutoff correlation
1 0.01 0 1000 -0.9 0 4 0.2021 1 0.01 0 1000 -0.9 0 3 0.5706 1 0.01 0 1000 -0.9 0 2 0.8769 2 0.01 0 1000 -0.9 0.3 4 0.3995 2 0.01 0 1000 -0.9 0.3 3 0.6799 2 0.01 0 1000 -0.9 0.3 2 0.8864 3 0.01 0 1000 -0.9 0.6 4 0.62 3 0.01 0 1000 -0.9 0.6 3 0.7709 3 0.01 0 1000 -0.9 0.6 2 0.8531 4 0.01 0 1000 -0.6 0 4 0.205 4 0.01 0 1000 -0.6 0 3 0.58 4 0.01 0 1000 -0.6 0 2 0.8773 5 0.01 0 1000 -0.6 0.3 4 0.4014 5 0.01 0 1000 -0.6 0.3 3 0.6827 5 0.01 0 1000 -0.6 0.3 2 0.8869 6 0.01 0 1000 -0.6 0.6 4 0.6181 6 0.01 0 1000 -0.6 0.6 3 0.776 6 0.01 0 1000 -0.6 0.6 2 0.8502 7 0.01 0 1000 -0.3 0 4 0.2084 7 0.01 0 1000 -0.3 0 3 0.5789 7 0.01 0 1000 -0.3 0 2 0.877 8 0.01 0 1000 -0.3 0.3 4 0.3999 8 0.01 0 1000 -0.3 0.3 3 0.6746 8 0.01 0 1000 -0.3 0.3 2 0.8824 9 0.01 0 1000 -0.3 0.6 4 0.6224 9 0.01 0 1000 -0.3 0.6 3 0.7678 9 0.01 0 1000 -0.3 0.6 2 0.8425 10 0.01 0 1000 0 0 4 0.19 10 0.01 0 1000 0 0 3 0.5669 10 0.01 0 1000 0 0 2 0.8763 11 0.01 0 1000 0 0.3 4 0.404 11 0.01 0 1000 0 0.3 3 0.6753 11 0.01 0 1000 0 0.3 2 0.8883 12 0.01 0 1000 0 0.6 4 0.6052 12 0.01 0 1000 0 0.6 3 0.7689 12 0.01 0 1000 0 0.6 2 0.8443 13 0.01 0 1500 -0.9 0 4 0.3574 13 0.01 0 1500 -0.9 0 3 0.6476 13 0.01 0 1500 -0.9 0 2 0.8926 14 0.01 0 1500 -0.9 0.3 4 0.4787 14 0.01 0 1500 -0.9 0.3 3 0.7314 14 0.01 0 1500 -0.9 0.3 2 0.8977 15 0.01 0 1500 -0.9 0.6 4 0.6623 15 0.01 0 1500 -0.9 0.6 3 0.7958 15 0.01 0 1500 -0.9 0.6 2 0.8401 16 0.01 0 1500 -0.6 0 4 0.3513 16 0.01 0 1500 -0.6 0 3 0.646 16 0.01 0 1500 -0.6 0 2 0.8951 17 0.01 0 1500 -0.6 0.3 4 0.4728 17 0.01 0 1500 -0.6 0.3 3 0.7341 17 0.01 0 1500 -0.6 0.3 2 0.8985 18 0.01 0 1500 -0.6 0.6 4 0.6491 18 0.01 0 1500 -0.6 0.6 3 0.7945 18 0.01 0 1500 -0.6 0.6 2 0.8407 19 0.01 0 1500 -0.3 0 4 0.367 19 0.01 0 1500 -0.3 0 3 0.6571 19 0.01 0 1500 -0.3 0 2 0.8897 20 0.01 0 1500 -0.3 0.3 4 0.4695 20 0.01 0 1500 -0.3 0.3 3 0.7355 20 0.01 0 1500 -0.3 0.3 2 0.9004 21 0.01 0 1500 -0.3 0.6 4 0.6568 21 0.01 0 1500 -0.3 0.6 3 0.7947 21 0.01 0 1500 -0.3 0.6 2 0.8391 22 0.01 0 1500 0 0 4 0.3722 22 0.01 0 1500 0 0 3 0.6566 22 0.01 0 1500 0 0 2 0.8943 23 0.01 0 1500 0 0.3 4 0.4745 23 0.01 0 1500 0 0.3 3 0.7278 23 0.01 0 1500 0 0.3 2 0.8946 24 0.01 0 1500 0 0.6 4 0.6529 24 0.01 0 1500 0 0.6 3 0.7951 24 0.01 0 1500 0 0.6 2 0.8404 25 0.01 0 2000 -0.9 0 4 0.4613 25 0.01 0 2000 -0.9 0 3 0.7304 25 0.01 0 2000 -0.9 0 2 0.8991 26 0.01 0 2000 -0.9 0.3 4 0.5551 26 0.01 0 2000 -0.9 0.3 3 0.7915 26 0.01 0 2000 -0.9 0.3 2 0.8977 27 0.01 0 2000 -0.9 0.6 4 0.6894 27 0.01 0 2000 -0.9 0.6 3 0.8012 27 0.01 0 2000 -0.9 0.6 2 0.8377 28 0.01 0 2000 -0.6 0 4 0.4717 28 0.01 0 2000 -0.6 0 3 0.7292 28 0.01 0 2000 -0.6 0 2 0.9036 29 0.01 0 2000 -0.6 0.3 4 0.5526 29 0.01 0 2000 -0.6 0.3 3 0.7815 29 0.01 0 2000 -0.6 0.3 2 0.8998 30 0.01 0 2000 -0.6 0.6 4 0.7032 30 0.01 0 2000 -0.6 0.6 3 0.8049 30 0.01 0 2000 -0.6 0.6 2 0.8387 31 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0 4 0.4678 31 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0 3 0.715 31 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0 2 0.8939 32 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.3 4 0.5525 32 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.3 3 0.7861 32 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.3 2 0.8994 33 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.6 4 0.7005 33 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.6 3 0.804 33 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.6 2 0.8399 34 0.01 0 2000 0 0 4 0.4594 34 0.01 0 2000 0 0 3 0.7167 34 0.01 0 2000 0 0 2 0.8992 35 0.01 0 2000 0 0.3 4 0.5481 35 0.01 0 2000 0 0.3 3 0.7883 35 0.01 0 2000 0 0.3 2 0.8981 36 0.01 0 2000 0 0.6 4 0.692 36 0.01 0 2000 0 0.6 3 0.8032 36 0.01 0 2000 0 0.6 2 0.8541
opt_B.plot_2d(show_best=10)
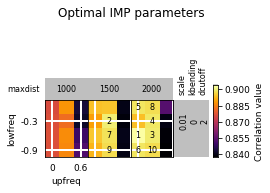
Refine optimization in a small region:
opt_B.run_grid_search(upfreq_range=(0, 0.3, 0.3), lowfreq_range=(-0.9, -0.3, 0.3),
maxdist_range=[1750],
dcutoff_range=[2, 3],
n_cpus=8)
Optimizing 61 particles num scale kbending maxdist lowfreq upfreq dcutoff correlation
1 0.01 0 1750 -0.9 0 3 0.6859 1 0.01 0 1750 -0.9 0 2 0.8985 2 0.01 0 1750 -0.9 0.3 3 0.7587 2 0.01 0 1750 -0.9 0.3 2 0.9 3 0.01 0 1750 -0.6 0 3 0.6879 3 0.01 0 1750 -0.6 0 2 0.8937 4 0.01 0 1750 -0.6 0.3 3 0.7521 4 0.01 0 1750 -0.6 0.3 2 0.8993 5 0.01 0 1750 -0.3 0 3 0.6857 5 0.01 0 1750 -0.3 0 2 0.9 6 0.01 0 1750 -0.3 0.3 3 0.7644 6 0.01 0 1750 -0.3 0.3 2 0.8981
opt_B.plot_2d(show_best=5)
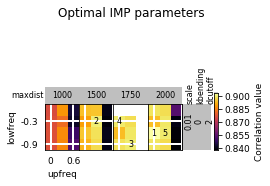
opt_B.run_grid_search(upfreq_range=(0, 0.3, 0.3), lowfreq_range=(-0.3, 0, 0.1),
maxdist_range=[2000, 2250],
dcutoff_range=[2],
n_cpus=8)
xx 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0 4.0 0.4678 xx 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.3 4.0 0.5525
Optimizing 61 particles num scale kbending maxdist lowfreq upfreq dcutoff correlation
1 0.01 0 2000 -0.2 0 2 0.9001 2 0.01 0 2000 -0.2 0.3 2 0.8989 3 0.01 0 2000 -0.1 0 2 0.901 4 0.01 0 2000 -0.1 0.3 2 0.8967 xx 0.01 0 2000 0 0 4.0 0.4594 xx 0.01 0 2000 0 0.3 4.0 0.5481 5 0.01 0 2250 -0.3 0 2 0.8962 6 0.01 0 2250 -0.3 0.3 2 0.8964 7 0.01 0 2250 -0.2 0 2 0.9024 8 0.01 0 2250 -0.2 0.3 2 0.9004 9 0.01 0 2250 -0.1 0 2 0.8992 10 0.01 0 2250 -0.1 0.3 2 0.9009 11 0.01 0 2250 0 0 2 0.9001 12 0.01 0 2250 0 0.3 2 0.8967
opt_B.plot_2d(show_best=5)
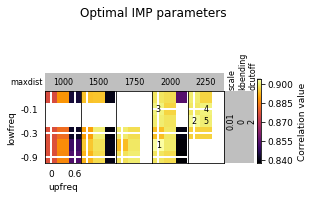
opt_B.run_grid_search(upfreq_range=(0, 0.3, 0.1), lowfreq_range=(-0.3, 0, 0.1),
n_cpus=8,
maxdist_range=[2000, 2250],
dcutoff_range=[2])
xx 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0 4.0 0.4678
Optimizing 61 particles num scale kbending maxdist lowfreq upfreq dcutoff correlation
1 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.1 2 0.898 2 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.2 2 0.8979 xx 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.3 4.0 0.5525 xx 0.01 0 2000 -0.2 0 2.0 0.9001 3 0.01 0 2000 -0.2 0.1 2 0.8908 4 0.01 0 2000 -0.2 0.2 2 0.8944 xx 0.01 0 2000 -0.2 0.3 2.0 0.8989 xx 0.01 0 2000 -0.1 0 2.0 0.901 5 0.01 0 2000 -0.1 0.1 2 0.8967 6 0.01 0 2000 -0.1 0.2 2 0.8941 xx 0.01 0 2000 -0.1 0.3 2.0 0.8967 xx 0.01 0 2000 0 0 4.0 0.4594 7 0.01 0 2000 0 0.1 2 0.9006 8 0.01 0 2000 0 0.2 2 0.8914 xx 0.01 0 2000 0 0.3 4.0 0.5481 xx 0.01 0 2250 -0.3 0 2.0 0.8962 9 0.01 0 2250 -0.3 0.1 2 0.8991 10 0.01 0 2250 -0.3 0.2 2 0.8957 xx 0.01 0 2250 -0.3 0.3 2.0 0.8964 xx 0.01 0 2250 -0.2 0 2.0 0.9024 11 0.01 0 2250 -0.2 0.1 2 0.8984 12 0.01 0 2250 -0.2 0.2 2 0.8993 xx 0.01 0 2250 -0.2 0.3 2.0 0.9004 xx 0.01 0 2250 -0.1 0 2.0 0.8992 13 0.01 0 2250 -0.1 0.1 2 0.9024 14 0.01 0 2250 -0.1 0.2 2 0.8959 xx 0.01 0 2250 -0.1 0.3 2.0 0.9009 xx 0.01 0 2250 0 0 2.0 0.9001 15 0.01 0 2250 0 0.1 2 0.9033 16 0.01 0 2250 0 0.2 2 0.895 xx 0.01 0 2250 0 0.3 2.0 0.8967
opt_B.plot_2d(show_best=5)
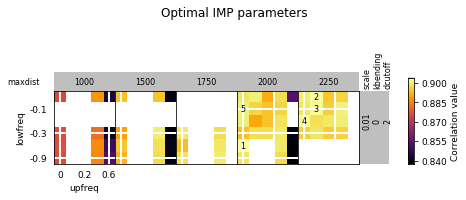
opt_B.get_best_parameters_dict()
{'scale': 0.01,
'kbending': 0.0,
'maxdist': 2000.0,
'lowfreq': -0.6,
'upfreq': 0.0,
'dcutoff': 2.0,
'reference': '',
'kforce': 5}
For the other replicate, we can reduce the space of search:
opt_PSC = PSC.optimal_imp_parameters(start=300, end=360, n_models=40, n_keep=20, n_cpus=8,
upfreq_range=(0, 0.3, 0.1),
lowfreq_range=(-0.3, -0.1, 0.1),
maxdist_range=(2000, 2250, 250),
dcutoff_range=[2])
Optimizing 61 particles num scale kbending maxdist lowfreq upfreq dcutoff correlation
1 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0 2 0.9309 2 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.1 2 0.9237 3 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.2 2 0.9177 4 0.01 0 2000 -0.3 0.3 2 0.9084 5 0.01 0 2000 -0.2 0 2 0.9268 6 0.01 0 2000 -0.2 0.1 2 0.9245 7 0.01 0 2000 -0.2 0.2 2 0.9159 8 0.01 0 2000 -0.2 0.3 2 0.9095 9 0.01 0 2000 -0.1 0 2 0.9283 10 0.01 0 2000 -0.1 0.1 2 0.9239 11 0.01 0 2000 -0.1 0.2 2 0.9136 12 0.01 0 2000 -0.1 0.3 2 0.9071 13 0.01 0 2250 -0.3 0 2 0.9285 14 0.01 0 2250 -0.3 0.1 2 0.9233 15 0.01 0 2250 -0.3 0.2 2 0.9165 16 0.01 0 2250 -0.3 0.3 2 0.9068 17 0.01 0 2250 -0.2 0 2 0.9294 18 0.01 0 2250 -0.2 0.1 2 0.9214 19 0.01 0 2250 -0.2 0.2 2 0.9154 20 0.01 0 2250 -0.2 0.3 2 0.9041 21 0.01 0 2250 -0.1 0 2 0.9304 22 0.01 0 2250 -0.1 0.1 2 0.9219 23 0.01 0 2250 -0.1 0.2 2 0.9157 24 0.01 0 2250 -0.1 0.3 2 0.9076
opt_PSC.plot_2d(show_best=5)
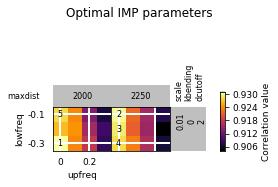
opt_PSC.get_best_parameters_dict()
{'scale': 0.01,
'kbending': 0.0,
'maxdist': 2000.0,
'lowfreq': -0.3,
'upfreq': 0.0,
'dcutoff': 2.0,
'reference': '',
'kforce': 5}

